Views: 1392
Since there are system, requirement, expectations, there are audits.Similar to financial compliance audits, we have those over suppliers as well and even more depending on markets and customer demands.
Audits are taken as important and powerful tools to drive supplier improvement activities and commonly in non-regulated industries those audits can be categorized and structured as below upside down pyramid diagram and generally (not absolutely) the topper ones are more formal, while the lower ones are more informal.
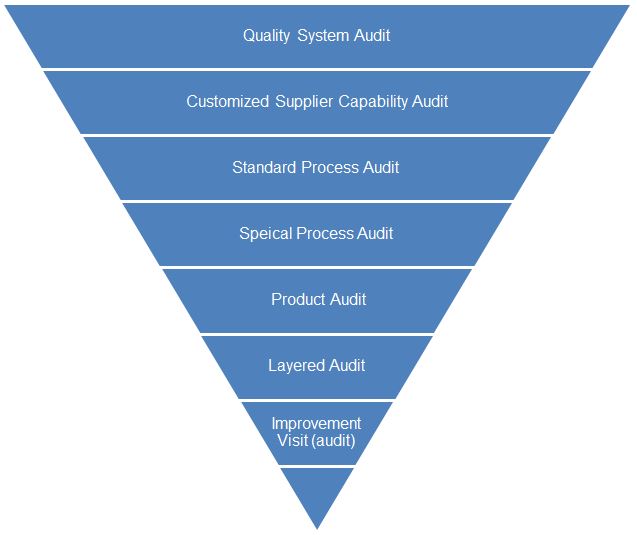
Though each one has individual names but still link to each other and may cross between some ones, and some more explanation are following:
- Quality System Audit
Usually it’s done at the beginning of setting up business relationship with suppliers to assess the compliance level to required Quality Management System, and in some organizations this can be replaced by reliable proof such as ISO 9001 certificates from reputable issuing bodies to simplify the process and reduce workload for suppliers and purchasers as well.In some companies, this is also conducted each year as regular routine to monitor the constant compliance.
- Customized Supplier Capability Audit
This varies among purchasing organizations, and different names are given to such audits, for examples like Supplier Screening Audit, Supplier Assessment, Supplier Capability Audit, etc. It’s customized by the purchasing organizations to “fit” the demands from all the stakeholders, and may combine the process control elements with quality management system. Some more purchasing organizations may even add Engineering Capability, Cost Control Capability, Risk Management, Recycling Management, Potential Business Relationship, Impact and Volume, furthermore nowadays it’s also very common to place aspects of Environmental Management, Social Responsibility, Occupational Health and Safety inside. That’s why usually the checklist will be very long and time taking for completing an audit.It would be good at the beginning to use Project team to perform the audits if there is no independent and capable quality resource available when you set up the process and then shift to be more independent and fair by quality staff after the formalization as transition.
- Standard Process Audit
Here I meant the VDA 6.3 Process Audit which was developed by Germany Automotive Association and though it’s targeted to be used for Automotive Industry but now is also adopted by some Germany companies especially when those German management from Automotive Industry joined other non-automtive industries. One possible reason is that the “Sponsors” have been used to the rigid tools and they do not like to redevelop a new tool and checklist which creating lots of discussions, arguments and justification in the organization.
- Special Process Audit
The Special Process Audit terminology comes from CQI-16 (Continuous Quality Improvement – 16)of AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group), where Manufacturing Process Audit is mentioned to focus on the Manufacturing Process and particularly some common and special processes were emphasized, such as Heat Treatment (CQI-9), Plating System (CQI-11), Coating (CQI-12),Welding System (CQI-15),Soldering System (CQI-17). The Process Flow Diagram (PFD), Control Plans, Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis (PFMEA) are usually used in such audits, as most of these documents are quite demanding for non-automotive industries, so as far as I know for non-automotive industries in China, they are not so popularly used in practice except some top Electronics companies, where they may develope their own Process Audit systems for some special processes.
- Product Audit
Product Audit usually is performed after Process Audit at Project Phasse and typically re-done regularly to ensure products consistently meeting the standards and/or specifications. There are standard requirement and guidelines in VDA 6.5. More introduction will be made in the sub-category of Product Audit page.
- Layerd Process Audit
Layer Process Audit is implemented by AIAG as CQI-8. The key focus is to ensure the daily process control are to the greatest extent awared of timely by all layers of quality influencers. Different level employees have to “audit” the process based on pre-defined items and schedules. So that delayed actions due to resource constraints will be quickly identified and addressed. It’s not that difficult and could be used in non-automotive industries as well.
- Improvement Audit (Visit)
Improvement visit is the most informal audit to my understanding.This can be done by any visitors for any purpose to suppliers, either for negotiation, general impress refresh, potential capability understanding, problem solving, engineering, commercial or project discussion,etc. It’s a kind of supplier development tools. Normally visitors do not develop individual reports to address the findings or suggestions but they may include or refer to those points in somewhere else. I would suggest you to read the “Rapid Plant Assessment” written by professor R.Eugene Goodson and posted on Havard Business Review issue May,2002. Though it’s more than 10 years old but it’s still very practicable.
Commonly some points should be noticed when you decide to implement some of above methodology:
- Clear Communication
Agreement or at least requirement should be given to suppliers in advance of establishing business relationship or awarding project.To many European and American customers from automotive industry, these are quite basic and common sense but actually when it comes to China, this must be pre-communicated otherwise this may cause confusions, embarrassment or even disputes.
- Clear Agenda
Very often when you come to China, you will be accompanied by your local staff and they shall pass your Agenda to your manufacturing suppliers. Consider if they do not know what will be your topics, how can they give you best support and get suppliers prepared.I strongly suggest you to ask your local representatives to review your agenda before finalizing it.
- Follow Agenda strictly
Some of you may come to China the first time or not so frequently, but this should not be the reason for you to change the agenda. In some cases I noticed the visitors come to China with agenda for Pilot Run Process Validation and was assumed to give a release for serial production, but finally after the visit, a System Audit report is received. This may give a messy message to suppliers that either the visitor is not professional or there is no clear Supplier Management System in your organization.
- Align the tools in group companies
In group companies, usually before all the processes are harmonized between sister companies, each company will have their own system to manage and audit suppliers. If the audit checklist or tools are not aligned before you start to them, then probably different persons may use different scoring system, which resulted in “big” score variance and reduce the “attention” of suppliers to the scores given to them. If you do not have a good database to share all this kind of reports, I would suggest you to double check with your Head Office coordinator or your local representatives as they usually get all the information and “troubles”, so that they are in the best position to give a solution or proposal.
Does it make any sense?
 粤ICP备2022015479号-1 All Rights Reserved © 2017-2023
粤ICP备2022015479号-1 All Rights Reserved © 2017-2023